Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimada, Taro; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Miwa, Kazuji; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
Nuclear regulatory inspection should be performed on the basis of the risk information during the decommissioning phase of the nuclear power plant. However, it is difficult because the methodology for quantitatively assessing the radiation exposure risk during decommissioning activities has not been established. Therefore, a decommissioning risk assessment code, DecAssess-R, has been developed based on the decommissioning safety assessment code, DecAssess, which creates event trees from initiating events and evaluates the radiation risk resulting from public exposure dose for each accident sequence. The assessment took into account that mobile radioactive inventories that can be easily dispersed in the work area, such as radioactive dust accumulated in HEPA filters attached to a contamination control enclosure, will fluctuate with the progress of the decommissioning work. Initiating events were selected based on the investigation of accidents and malfunctions during dismantling, disassembly, and component replacement activities around the world, and event trees were created from the initiating events to indicate the progress scenario. The frequencies of occurrence were determined with reference to general industry data in addition to the above accidents and malfunctions, and the probabilities of event progression were determined with reference to failure data during the operation phase. The exposure risks during dismantling of components in the reference BWR were evaluated. As a result, the public exposure dose was maximum in case of fire during dismantling of reactor internals and fire spread to combustibles and filters, including radioactivity temporarily stored in the work area. The exposure risk was also maximum because the probability of occurrence of this accident sequence was greater than that of other scenarios.
Dohi, Terumi; Omura, Yoshihito*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kanaizuka, Seiichi*; Nakama, Shigeo; Iijima, Kazuki
PLOS ONE (Internet), 16(5), p.e0251828_1 - e0251828_16, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hagiwara, Hiroki; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Konishi, Hiromi*; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 220-221, p.106294_1 - 106294_9, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)Matsuda, Norihiro; Konno, Chikara; Ikehara, Tadashi; Okumura, Keisuke; Suyama, Kenya*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-003, 33 Pages, 2020/03
Data handling modules for the radioactivity calculation code, ORIGEN-S, are developed for the reliable evaluations of radioactivity inventory. By using these modules, an activation cross-section data library for the ORIGEN-S code is updated easily and effectively based on a facility-specific neutron spectrum and multi-group neutron activation cross-section library for decommissioning of nuclear facilities, MAXS2015. In order to guarantee the reliability of the radioactivity calculations, functions of data verification in a visual way and numerical comparison between before and after the data processing are also prepared.
Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Nakayama, Takuya; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
In December 2016, the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-toge) announced new concept of "Uranium and Environmental Research Platform". As part of the concept, uranium waste engineering research are now undergoing. The objective of the research is to establish the processing technology for safely and reasonable disposal of uranium waste. In particular, estimation of the amount of uranium and harmful substances and development of technologies to reduce their concentration in the waste to the permissive level for the disposal in shallow ground disposal are needed. We are now developing the technologies to reduce the concentration of uranium and harmful substances shown below. (1) Survey on uranium inventory. Uranium waste is now stored in 10-odd thousands of 200 L drums. We are surveying amount and chemical form of uranium in the drums. (2) Development of decontamination technology of metal and concrete waste. We are investigating decontamination methods for metals and concrete contaminated with uranium. (3) Development of technologies to remove, detoxify and fix the harmful substances. We are surveying the types and amounts of harmful substances in waste. In addition, we are investigating the method to remove, detoxify, and fix harmful substances. (4) Measurement technology of uranium radioactivity. We are investigating and examining ways to improve the quantitative accuracy of measurement and shorten the measurement time. (5) Development of uranium removal technology from sludge. We are investigating new processing method to remove uranium from sludge which is applicable for several kind of sludge. The results of these technological developments and environmental research will be reflected to "small-scale field test" and "disposal demonstration test" which are planned for demonstration of the uranium waste disposal technology.
Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Oi, Takao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.1933 - 1942, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:85.7(Nuclear Science & Technology) Cs on surfaces of buildings and building lots
Cs on surfaces of buildings and building lotsYoshimura, Kazuya; Fujiwara, Kenso; Saito, Kimiaki
KEK Proceedings 2016-8, p.67 - 71, 2016/10
This study evaluated the  Cs inventory (Bq m
Cs inventory (Bq m ) on urban surfaces for eleven buildings and building lots in evacuation zone, and relative
) on urban surfaces for eleven buildings and building lots in evacuation zone, and relative  Cs inventory was obtained by dividing with the initial inventory on plane permeable field around the studied building. The relative
Cs inventory was obtained by dividing with the initial inventory on plane permeable field around the studied building. The relative  Cs inventory was highest at plane permeable field (0.92), followed by paved ground (0.28) on January 13, 2015. Other surfaces such as roof, wall and window showed obviously small values less than 0.1, indicating that the contamination level of buildings was limited four years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Roof and paved ground showed different relative
Cs inventory was highest at plane permeable field (0.92), followed by paved ground (0.28) on January 13, 2015. Other surfaces such as roof, wall and window showed obviously small values less than 0.1, indicating that the contamination level of buildings was limited four years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Roof and paved ground showed different relative  Cs inventories from those in the case of Europe after the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident, suggesting the importance of local parameterization considering the factors affects to the variation of relative
Cs inventories from those in the case of Europe after the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident, suggesting the importance of local parameterization considering the factors affects to the variation of relative  Cs inventory.
Cs inventory.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:81.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.452 - 455, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.6(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium behavior released in ITER hot cell has been investigated numerically. Tritium behavior was evaluated by a combined analytical methods of a tritium transport analysis with the one dimensional diffusion model in the multi-layer wall (concrete and epoxy paint) and a tritium concentration analysis with the complete mixing model by the ventilation in the hot cell under the simulated hot cell operational conditions. As the results, tritium concentration in the hot cell volume decreases rapidly from 300 DAC (Derived Air Concentration) less than 1 DAC in several days after removing the tritium release source. Tritium inventory in the wall is estimated to be about 0.1 PBq for 20 years operation. On the other hand, Tritium permeation through the epoxy painted concrete wall will be negligible. Finally, as to the effect of epoxy paint on the tritium permeation and inventory, it is found that the epoxy paint can reduce tritium inventory by about two orders of magnitude relative to bare concrete wall.
Matsuhiro, Kenjiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.625 - 628, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho*; Matsuhiro, Kenjiro; Fischer, U.*; Hayashi, Takumi; Mori, Seiji*; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishitani, Takeo; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Simakov, S.*; et al.
JAERI-Review 2005-005, 40 Pages, 2005/03
The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is being jointly planned to provide an accelerator-based Deuterium-Lithium (Li) neutron source to produce intense high energy neutrons (2 MW/m ) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm
) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm ) for testing the candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as 7Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal and thermal stress analyses, the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop, and the tritium inventory and permeation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAERI activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2004.
) for testing the candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as 7Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal and thermal stress analyses, the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop, and the tritium inventory and permeation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAERI activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2004.
Povinec, P. P.*; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Burr, G. S.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; Liong Wee Kwong, L.*; Togawa, Orihiko
Radiocarbon, 46(2), p.583 - 594, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:32.5(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Higashijima, Satoru; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Horikawa, Toyohiko*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Miya, Naoyuki; Nishi, Masataka; Konishi, Satoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 70(2), p.163 - 173, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish the effective and conventional in-vessel tritium removal method, glow discharge methods, usually used as wall conditioning, have been applied and examined in vacuum vessel of JT-60U for tritium removal characteristics and kinetics. Release rates of all hydrogen isotopes as well as hydrocarbons from JT-60U vacuum vessel induced by Glow Discharge Cleaning (GDC) with He and H were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H
were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H
GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H
glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H GDC at 573 K.
GDC at 573 K.
Akutsu, Atsushi; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Sukegawa, Takenori; Shimada, Taro
JAERI-Tech 2003-090, 75 Pages, 2004/01
The Japan Research Reactor No.1 (JRR-1) that was constructed first in Japan was permanently shut down after operation from 1957 to 1968. At present, the reactor part is in safe store conditions. The JRR-1 facility is being used as an exhibition room for the time being, and will be dismantled in the future. In consideration of future dismantling of the facility, the radioactive inventory in reactor part was calculated using computer codes that are Two-Dimensional Discrete Ordinates Transport Code (DORT) and Oak Ridge Isotope Generation and Depletion Code (ORIGEN-MD). The average concentration of radioactivity is estimated to be 6.40
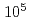 Bq/g in the core tank as of April, 2002. It is also expected that the low level waste (LLW) weights approximately 400kg and very low level waste (VLLW) weights approximately 14,000kg, and the waste which doesn't need to deal as a radioactive material weights approximately 250,000kg.
Bq/g in the core tank as of April, 2002. It is also expected that the low level waste (LLW) weights approximately 400kg and very low level waste (VLLW) weights approximately 14,000kg, and the waste which doesn't need to deal as a radioactive material weights approximately 250,000kg.
Ito, Toshimichi; Aramaki, Takafumi; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kobayashi, Takuya; Senju, Tomoharu*; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Karasev, E. V.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 68(3), p.249 - 267, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:62.84(Environmental Sciences)The anthropogenic radionuclides,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  Pu, in the seawater column of the Japan Sea were measured during 1997-2000. The vertical profiles of radionuclide concentrations showed their typical features; exponential decrease with depth for the
Pu, in the seawater column of the Japan Sea were measured during 1997-2000. The vertical profiles of radionuclide concentrations showed their typical features; exponential decrease with depth for the  Sr and
Sr and  Cs and surface minimum - subsurface maximum for the
Cs and surface minimum - subsurface maximum for the  Pu, and there are no substantial differences between the present study and the previous ones. The area-averaged concentrations and the inventories of radionuclides in the Japan Sea are higher than those in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. In the spatial distributions, high inventory area extends and intrudes from the Japan Basin into the Yamato Basin. It is suggested that radionuclides sink by the vertical transport occurring mainly in the Japan Basin then advect into the Yamato Basin after detouring around the Yamato Rise, and finally, they are accumulated in the deep seawater of the Japan Sea.
Pu, and there are no substantial differences between the present study and the previous ones. The area-averaged concentrations and the inventories of radionuclides in the Japan Sea are higher than those in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. In the spatial distributions, high inventory area extends and intrudes from the Japan Basin into the Yamato Basin. It is suggested that radionuclides sink by the vertical transport occurring mainly in the Japan Basin then advect into the Yamato Basin after detouring around the Yamato Rise, and finally, they are accumulated in the deep seawater of the Japan Sea.
Kosaku, Yasuo; Kuroda, Toshimasa*; Enoeda, Mikio; Hatano, Toshihisa; Sato, Satoshi; Sato, Shinichi*; Osaki, Toshio*; Miki, Nobuharu*; Akiba, Masato
JAERI-Tech 2003-058, 69 Pages, 2003/06
The design of the breeding blanket in ITER applies pebble bed breeder in tube (BIT) surrounded by multiplier pebble bed. It is assumed to use the same module support mechanism and coolant manifolds and coolant system as the shielding blankets. This work focuses on the verification of the design of the breeding blanket, from the viewpoints which is especially unique to the pebble bed type breeding blanket, such as, tritium breeding performance, tritium inventory and release behavior and thermo-mechanical performance of the ITER breeding blanket.
Yoshida, Hiroshi; Glugla, M.*; Hayashi, Takumi; L sser, R.*; Murdoch, D.*; Nishi, Masataka; Haange, R.*
sser, R.*; Murdoch, D.*; Nishi, Masataka; Haange, R.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 61-62, p.513 - 523, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER tritium plant is composed of tokamak fuel cycle systems, tritium confinement and detritation systems. The tokamak fuel cycle systems, composed of various tritium sumsystems such as vacuum vessel cleaning gas processing, tokamak exhaust processing, hydrogen isotope separation, fuel storage, mixing and delivery, and external tritium receiving and long-term storage, has been designed to meet not only ITER operation scenarios but safety requirements (minimization of equipment tritium inventory and reduction of environmental tritium release at different off-normal events and accident scenarios). Multiple confinement design was employed because tritium easily permeates through metals (at  150
150  C) and plastics (at ambient temperature) and mixed with moisture in room air. That is, tritium process equipment and piping are designed to be the primary confinement barrier, and the process equipments (tritium inventory
C) and plastics (at ambient temperature) and mixed with moisture in room air. That is, tritium process equipment and piping are designed to be the primary confinement barrier, and the process equipments (tritium inventory  1 g) are surrounded by the secondary confinement barrier such as a glovebox. Tritium process rooms, which contains these facilities, form the tertiary confinement barrier, and equipped with emergency isolation valves in the heating ventillation and air conditioning ducts as well as atmosphere detritiation systems. This confinement approach has been applied to tokamak building, tritium building, and hotcell and radwaste building.
1 g) are surrounded by the secondary confinement barrier such as a glovebox. Tritium process rooms, which contains these facilities, form the tertiary confinement barrier, and equipped with emergency isolation valves in the heating ventillation and air conditioning ducts as well as atmosphere detritiation systems. This confinement approach has been applied to tokamak building, tritium building, and hotcell and radwaste building.
Iwai, Yasunori; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nishi, Masataka; Willms, R. S.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(6), p.661 - 669, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:65.6(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sukegawa, Takenori; Hatakeyama, Mutsuo; Yanagihara, Satoshi
JAERI-Tech 2001-058, 81 Pages, 2001/09
In general, neutron transport and activation calculation codes are used for residual radioactive inventory estimation; however, it is essential to verify calculations by measurement results because of geometrical complexity of the reactor and so on. The comparison between measured and calculated radioactivity in the JPDR core components showed a relatively good agreement (factor of 2), and it was cleared that water content and weight ratio of steel bars to concrete materials significantly influenced the neutron flux distribution in the biological shield (factor of 2-10 error). The measured radioactivity inside of the reactor pressure vessel wall and at the inner part of the biological shield was compared in detail with the calculations to verify the methodology applied to calculations of radioisotope production. Then it was found that the radioactive inventory could be estimated accurately with combination of calculations and measurement of radioactivity in samples and dose rate distribution for planning of dismantling activities.
Iwai, Yasunori; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2001-027, 29 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English